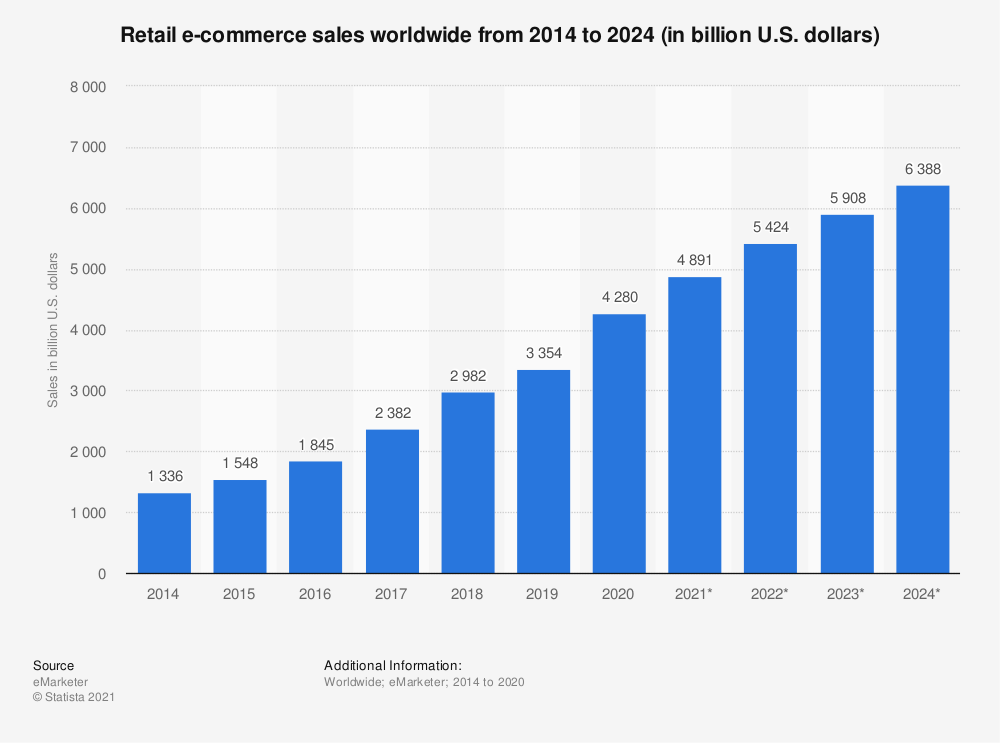
With the discovery of the Internet, more and more people get online. In 2021, the number of Internet users globally has reached a 7.83billion, and nearly 60% of the world’s total population is using the Internet. The number is still increasing, with an annual growth rate of 7% (Datareportal, 2021). The huge number of Internet users provides an excellent platform for the development of e-commerce. Especially in 2020, we are faced with COVID-19. As a large number of outdoor activities are banned, e-commerce has ushered in the most rapid development year. In 2020, retail e-commerce sales alone will reach 4280 billion U.S. dollars, an increase of 27% compared to 2019 (eMarketer, 2020). The growth of e-commerce has brought a lot of demand for express delivery. In 2018, the global express delivery volume reached 100 billion, with an annual growth rate of 5%. (Apex Insight, 2019)
The last-mile logistic refers to The last transportation distance of The final customer interaction. It largely determines whether the user experience is good or not. (Al-Nawayseh et al. 2013). The last mile of transport is the most expensive part of the entire express transport process for the same unit distance, accounting for 28 per cent of the total cost. (Zenezini et al., 2018). Low delivery efficiency, poor delivery service quality, and high delivery costs have become bottlenecks restricting express delivery development (Yu, 2019).
In response to some last-mile express delivery problems, the express company has implemented some solutions. But these solutions also have their unique shortcomings while solving the problem.
Traditional way: hire a courier to deliver the package
(Yu, 2019)
By hiring a courier, let them deliver the courier during working hours as required. This is currently the most used form.
Advantages:
- Effectively guarantee the safety of the package
- Guarantee the average timeliness
Disadvantages:
- The delivery time is not flexible, and it is easy to produce a second delivery date
- Low competitive pressure leads to poor service awareness and poor customer experience
- High cost
- Insufficient staff during peak period, and idle staff during underestimation period
Paid franchise form: express delivery point
Through the franchise form, merchants can rent a store close to the user as a temporary storage point for express delivery, and the user can pick up the goods at a suitable time. This form is widely used in China. This is mainly due to China’s densely populated population, and one express storage point can often cover many customers.
Advantages:
- Customer pickup time is relatively free
- Courier companies have lower costs
Disadvantages:
- Uncontrollable operating hours at storage locations may lead to a worse user experience
- High labour costs and high rental prices
- Irregular management
- Limited coverage radius
User pickup: Express locker
(Ji, 2019)

Build a professional express vault. The courier can put the courier in it, and the user can receive his package through the verification code on the mobile phone.
Advantages:
- Free pickup time, almost no secondary delivery
Disadvantages:
- high cabinet cost, subsequent electricity charges, rent, etc
- The size and quantity of storage couriers are limited
- The issue of charges after late pickup
- Limited coverage radius
Delivery in remote suburbs: paid ride-hailing
This is a relatively special mode of transportation, which mainly exists in fairly remote suburbs. When the number of couriers in a remote area is very small, the courier company cannot specifically arrange courier delivery personnel. It will cooperate with local drivers to help them deliver the goods.
Advantages:
- Compared with the traditional model, the cost is reduced
Disadvantages:
- Very low standardization
- Customers often face additional express charges
- The express delivery is less safe
cooperative urban logistics: a courier company that focuses on last-mile delivery
(Chu, 2020)
Some competing courier companies have tried to cooperate with an ordinary but independent agency to deliver last-mile packages in recent years.
Advantages:
- Reduced cost of centralized delivery of packages
Disadvantages:
- The priority delivery rights in the model are difficult to negotiate
- It isn’t easy to gain the trust of the courier company
High-tech application: drone transportation
(ARK invest, 2021)
Use drones to transport goods. This is the direction of future development and is currently the most promising model. But at the same time, because drone technology is still developing, this technology may not be able to achieve full coverage in the short term.
Advantages:
- Compared with people, the time is freer.
- The service can be better.
Disadvantages:
- The current cost is too high.
- It is in the trial stage and cannot be used in large quantities.
- Some technologies are not mature enough.
In this issue, we discussed the current modes of express delivery and their advantages and disadvantages. We will find that they have left some problems unresolved. In the next issue, we will delve into a new model and its application in reality.
Continue reading: Sharing Economy in Express: Using On-Demand Workers to Participate in Terminal Logistics Delivery.
Reference:
eMarketer. (July 19, 2017). Number of digital buyers worldwide from 2014 to 2021 (in billions) [Graph]. In Statista. Retrieved March 31, 2021, from https://www.statista.com/statistics/251666/number-of-digital-buyers-worldwide/
eMarketer. (December 12, 2020). Retail e-commerce sales worldwide from 2014 to 2024 (in billion U.S. dollars) [Graph]. In Statista. Retrieved March 31, 2021, from https://www.statista.com/statistics/379046/worldwide-retail-e-commerce-sales/
Brown, J. R., & Guiffrida, A. L. (2014). Carbon emissions comparison of last mile delivery versus customer pickup. International Journal of Logistics Research and Applications, 17(6), 503-521.
Goodman, R. W. (2005). Whatever you call it, just don’t think of last-mile logistics, last. Global Logistics & Supply Chain Strategies, 9(12).
Ji, S. F., Luo, R. J., & Peng, X. S. (2019). A probability guided evolutionary algorithm for multi-objective green express cabinet assignment in urban last-mile logistics. International Journal of Production Research, 57(11), 3382-3404.
Zhang, Y., Fan, X., & Zhou, L. (2019, March). Analysis and research on the “last mile” distribution innovation model of e-commerce express delivery. In Journal of Physics: Conference Series (Vol. 1176, No. 4, p. 042044). IOP Publishing.
Ko, S. Y., Cho, S. W., & Lee, C. (2018). Pricing and collaboration in last mile delivery services. Sustainability, 10(12), 4560.
Apex Insight. (2019). Global parcel delivery market insight report 2019. Retrieved March 2020, from https://www.apex-insight.com/product/global-parcel-delivery-market
Zenezini, G., Lagorio, A., Pinto, R., De Marco, A., & Golini, R. (2018). The collection-and-delivery points implementation process from the courier, express and parcel operator’s perspective. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 51(11), 594-599.
Chun, S. Y., Kleywegt, A. J., & Shapiro, A. (2017). When friends become competitors: the design of resource exchange alliances. Management Science, 63(7), 2127-2145.
Jin, X., Park, K. T., & Kim, K. H. (2019). Storage space sharing among container handling companies. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, 127, 111-131.
Chu, X., Liu, J., Ren, L., & Gong, D. (2020). Optimal contract design with a common agency in last-mile logistics. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, 139, 101956.
ARK invest (2021). Big Ideas 2021. In ARK invest. Retrieved January 26, 2021, from https://ark-invest.com/big-ideas-2021/
